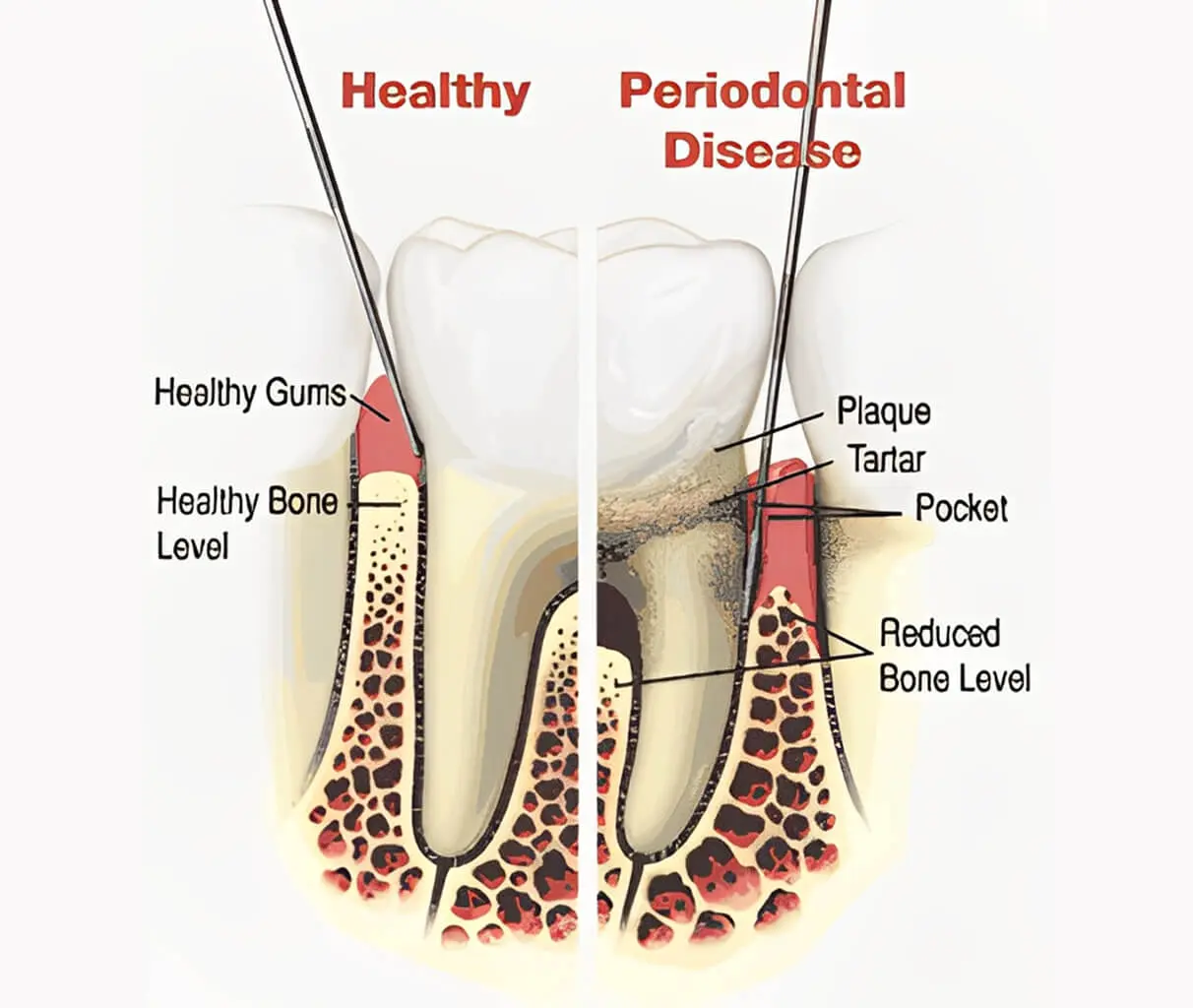
Periodontal Disease - Description & Process Dr. Sam Naim - Encino, CA
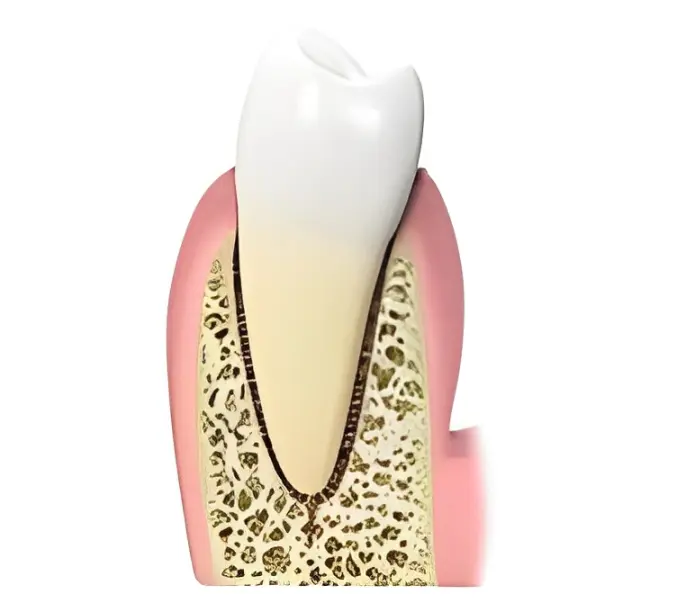
The main cause of periodontal disease is bacteria in the form of a sticky, colorless plaque that constantly forms on your teeth. Your body reacts to these bacteria with an inflammatory response.
Progression to Periodontitis
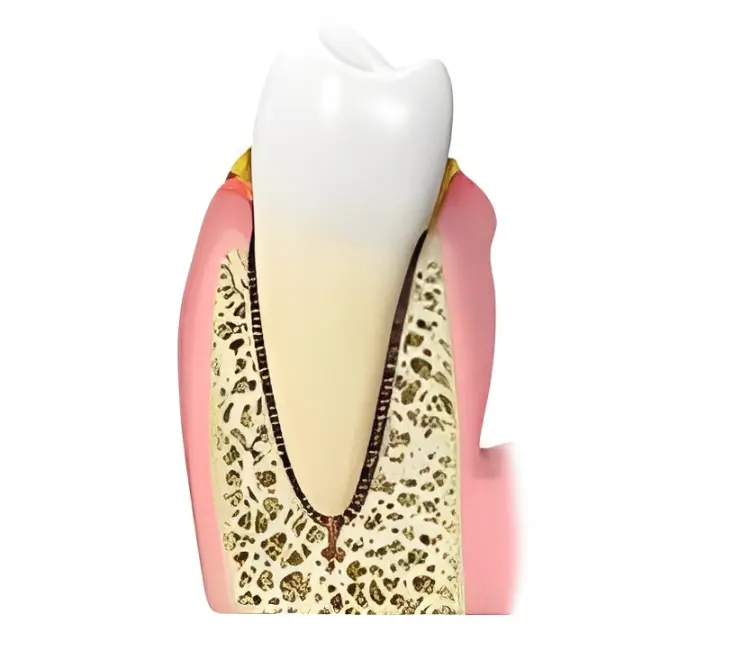
If left untreated, this inflammatory response can become a chronic inflammatory condition called Periodontitis. This is the condition where your body creates inflammatory tissue that had grown between your teeth and healthy gum tissue and has caused your tissues to become inflamed, swollen, and easily bleed when you brush or floss.
Periodontal Disease: Risks and Symptoms
Bone Loss & Tooth Mobility
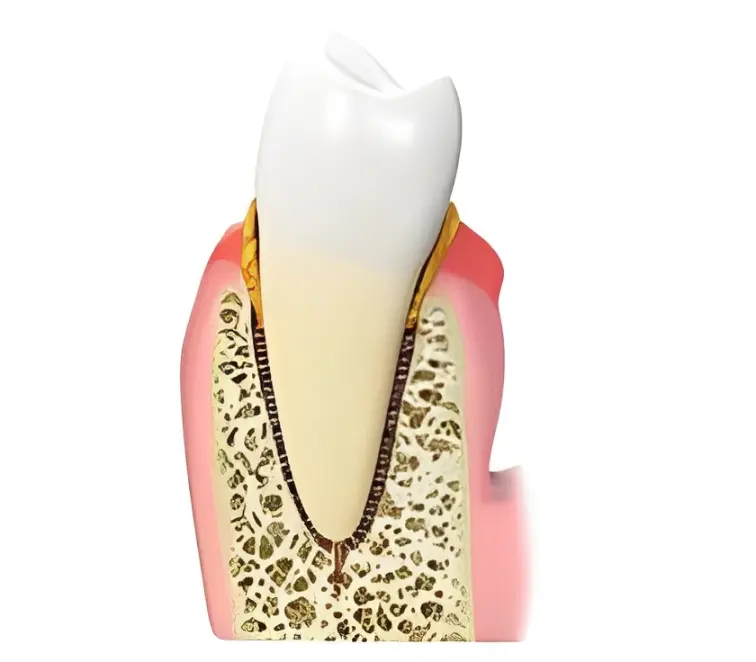
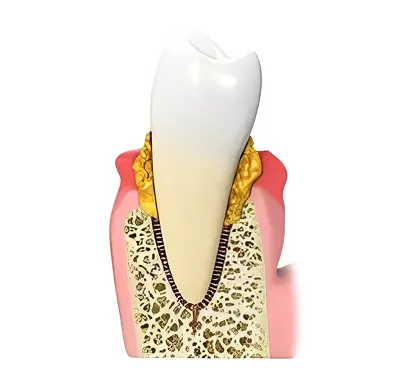
This inflammatory tissue slowly detaches the gums from the tooth surface until it reaches the bone surrounding and supporting your teeth. It then proceeds to erode away the bone until the teeth have lost substantial bone and gum tissue, resulting in tooth mobility. If teeth become significantly mobile, they may need to be extracted (removed).
Systemic Health Risks
Many other factors can cause periodontal (gum) disease or influence its progression. An individual may have an aggressive inflammatory response to the presence of bacterial plaque around the teeth. This can lead to advanced (aggressive) progression of gum tissue and bone loss, even with little presence of bacterial plaque. Periodontal disease can increase your risk of heart attack, stroke, diabetes, preterm low birth weight pregnancy. This is because Periodontal Disease is a chronic inflammatory condition. The constant inflammation in your gums has direct access to your bloodstream, granting access to these inflammatory disease factors to your bloodstream, which can then gain access to your heart, coronary arteries, blood vessels, and other organs of your body thereby creating increased risk of these other systemic diseases.
Silent Symptoms & Early Detection
Many people are unaware that they even have this condition as it does not create symptoms beyond swollen gum tissue, bleeding gums, recessed gums, or tooth mobility. Often, there is little to no pain present when someone has Periodontal disease. A consultation with a Periodontist is often necessary to determine if this condition exists. Schedule a consultation today to find out if you are at risk of having Periodontal Disease.